Abstract
Pts with R/R LBCL had rapid and durable responses with liso-cel, a CD19-directed chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T cell therapy. Previous qualitative research showed high perceptions of unmet pretreatment needs and largely positive pt experiences immediately after liso-cel infusion (Interviews 1-3; Siddiqi et al. Blood 2020;136 (suppl 1):22-23). We expanded our study to explore pt-perceived benefits and drawbacks after liso-cel treatment, up to 3 months.
Pts in 2 ongoing phase 2 trials (TRANSCEND WORLD [NCT03484702] and PLATFORM [NCT03310619]) had the option to participate in a series of semi-structured guided interviews that included several closed-ended questions. Transcribed audio recordings were analyzed using the qualitative software package MAXQDA 2020. Inter-coder agreement exercises evaluated and ensured sufficient reliability. Analyses included thematic analysis, quantitative descriptive analysis of closed-ended items, and qualitative longitudinal analysis. The longitudinal analysis assessed changes in patients' physical functioning across three months following treatment. Change over time was conceptualized in terms of improvement, worsening, or stability. The direction of change was transformed into a categorical variable to enable a descriptive quantitative analysis. Closed-ended items assessed benefits and negative aspects of liso-cel treatment on a scale from 0 (no) to 10 (tremendous) and whether benefits outweighed negative aspects on a 5-point Likert scale ranging from "benefits greatly outweighed" to "negatives greatly outweighed." Results at Months 1 (Interview 4), 2 (Interview 5), and 3 (Interview 6) after CAR T cell infusion are presented.
In total, 87 interviews (36, 29, and 22 interviews at Months 1, 2, and 3 after CAR T cell infusion, respectively) were analyzed across 40 pts in the United States and Europe, representing 34% of all participating pts by Month 3 (n = 118), or 50% of the 81 pts who received infusion by the same dates. Mean age of pts was 62.8 years; 70% were male. Most pts who described the infusion (27/29 [93%]) reported an overall positive impression, generally noting ease of, and time needed for, infusion. Common pt-reported side effects post infusion were fever (17/40 [43%]), weakness (13/40 [33%]), fatigue, and loss of appetite (8/40 [20% each]), which typically resolved during the first month. Overall, pts reported more benefits of liso-cel compared with other treatment options. Among pts who made comparisons between liso-cel and other available therapies (eg, chemotherapy, unspecified/other treatments, or stem cell transplantation), the percentage of pts reporting advantages were 90%, 100%, and 89%, respectively, whereas disadvantages were reported by 20%, 9%, and 11% of pts, respectively; 55% of pts who made comparisons to any prior treatment emphasized that liso-cel had a better side effect profile, others mentioned efficacy, infusion administration, or recovery time. At each time point, > 50% of respondents reported a benefits score within 8 and 10, and mean (standard deviation) scores across those who provided a numeric rating ranged from 8.42 (2.10) at Month 1 to 8.66 (1.38) at Month 3. The most common response across all interviews was 0/10 (no negative aspects).
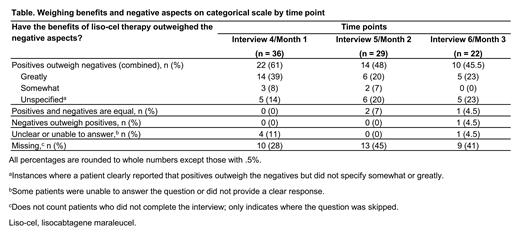
A small number (4/40 [10%]) considered the safety monitoring period after infusion a drawback compared with chemotherapy. Across 3 time points, 77%-88% of responders reported that the benefits of liso-cel outweighed any negative aspects (Table). Of pts asked if they would make the same decision to receive liso-cel therapy, knowing what they know now, and whether they would recommend the treatment to pts like them, 20/36 (56%), 20/29 (69%), and 17/22 (77%) answered "yes" at Months 1, 2, and 3, respectively. Three months after receiving treatment, 38% of patients were determined to have improved in terms of physical functioning since baseline, whereas 33% remained stable in this domain and 20% declined.
This study provides insight into pt experiences with liso-cel from the first clinical trials of CAR T cell therapy with embedded pt interviews. It is yet unknown for some patients whether they were responsive to liso-cel, however most reported positive experiences, found it more tolerable than prior therapies, few considered postinfusion safety monitoring a drawback, and indicated they would still choose liso-cel if they had to make the decision again.
Siddiqi: Juno Therapeutics: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; BeiGene: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; Celgene: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; BMS: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; Kite Pharma: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Pharmacyclics LLC, an AbbVie Company: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; Oncternal: Research Funding; Janssen: Speakers Bureau; TG Therapeutics: Research Funding; AstraZeneca: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Speakers Bureau. Jaeger: Janssen: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Gilead: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Norvartis: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; BMS/Celgene: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Roche: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Moshkovich: ICON plc: Current Employment. Braverman: BMS: Current Employment, Current equity holder in publicly-traded company. Liu: Bristol Myers Squibb: Current Employment, Current equity holder in publicly-traded company. Lanar: Roche: Consultancy; BMS: Consultancy; ICON plc: Current Employment. Miera: ICON Clinical Research: Current Employment. Salles: Novartis: Consultancy; Velosbio: Consultancy; Rapt: Consultancy; Regeneron: Consultancy, Honoraria; Takeda: Consultancy; Allogene: Consultancy; Morphosys: Consultancy, Honoraria; Miltneiy: Consultancy; Loxo: Consultancy; Kite/Gilead: Consultancy; Janssen: Consultancy; Ipsen: Consultancy; Incyte: Consultancy; Genmab: Consultancy; Genentech/Roche: Consultancy; Debiopharm: Consultancy; Epizyme: Consultancy, Honoraria; BMS/Celgene: Consultancy; Beigene: Consultancy; Abbvie: Consultancy, Honoraria; Bayer: Honoraria.